What Does Physiotherapy Do?
Physiotherapy, often abbreviated as PT, is a healthcare profession that focuses on helping individuals restore, maintain, and improve their physical mobility, strength, and function. Through a combination of movement exercises, manual therapy, and education, physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation process for individuals recovering from injury, illness, or surgery. But what exactly does physiotherapy do, and why is it so essential?
This article will explore the fundamental principles of physiotherapy, its various treatments, how it helps different conditions, and the overall impact on patient well-being. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of the vital role that physiotherapy plays in the healthcare system.
Do You Know About: Physiotherapy Exercises for Shoulder Pain: A Comprehensive Guide – Call My Physio
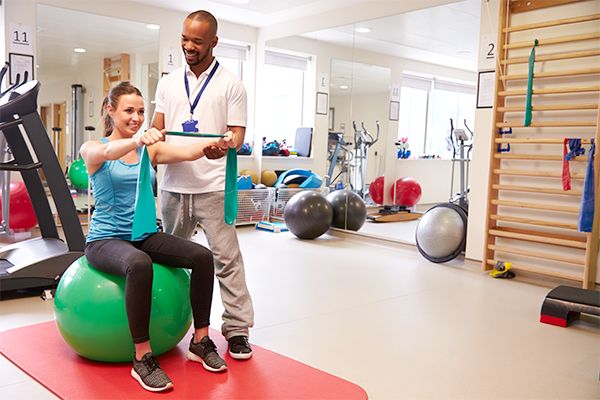

What Is Physiotherapy?
Physiotherapy is a branch of healthcare that assesses, diagnoses, and treats movement disorders arising from illness, injury, or disability. Its primary aim is to restore a person’s functional ability and quality of life through physical intervention, rehabilitation, and prevention strategies.
Physiotherapists are licensed professionals trained to evaluate musculoskeletal, neurological, and cardiopulmonary issues and offer tailored treatment plans. These treatments include exercises, manual therapy, electrotherapy, and patient education to manage pain, prevent injury, and promote overall health.
How Does Physiotherapy Work?
Physiotherapy works by improving movement and strength in affected areas of the body. Physiotherapists use a wide range of techniques and modalities to address various health concerns. Some key components include:
- Assessment and Diagnosis: The first step involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s physical condition, including movement patterns, muscle strength, joint function, and overall mobility.
- Treatment Planning: Based on the assessment, a personalized treatment plan is created to address the specific needs of the patient. This plan may involve exercises, manual techniques, and lifestyle modifications.
- Exercise Therapy: One of the core components of physiotherapy is exercise. These exercises are designed to improve strength, flexibility, coordination, and endurance. They are tailored to the individual’s condition, whether they are recovering from surgery or dealing with a chronic illness.
- Manual Therapy: Physiotherapists use hands-on techniques such as joint mobilization, soft tissue massage, and manipulation to relieve pain, improve mobility, and promote healing.
- Education and Prevention: Physiotherapists provide education on posture, movement, and ergonomics to help prevent future injuries and manage chronic conditions effectively.
- Rehabilitation: Physiotherapy is an essential part of rehabilitation after surgeries like knee replacements, hip replacements, or fractures, helping patients regain mobility and independence.
Benefits of Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is highly beneficial for people of all ages with various health conditions. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Pain Management
Physiotherapy is effective in managing and reducing both acute and chronic pain. Through targeted exercises and manual therapy, it can alleviate discomfort from musculoskeletal issues like arthritis, back pain, neck pain, and sciatica.
2. Improved Mobility and Flexibility
Physiotherapy helps individuals regain or improve their mobility. This is particularly beneficial for those recovering from surgery or injury, or for elderly patients who may experience reduced mobility due to age-related changes.
3. Recovery from Injury
Injuries from sports, accidents, or falls can severely limit a person’s movement and ability to perform daily activities. Physiotherapists create rehabilitation programs that help speed up recovery, restore function, and prevent future injuries.
4. Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
Post-operative recovery often requires extensive rehabilitation to regain strength, flexibility, and function. Physiotherapy is critical in this process, helping patients recover faster and more effectively after surgeries such as joint replacements, ligament repairs, and spinal surgeries.
5. Management of Chronic Conditions
For individuals with chronic conditions like arthritis, multiple sclerosis, or heart disease, physiotherapy plays a vital role in managing symptoms and maintaining overall health. It helps reduce pain, improve mobility, and enhance the quality of life for those dealing with long-term conditions.
6. Prevention of Injury
Physiotherapists provide valuable advice on injury prevention. By teaching patients proper techniques for lifting, exercising, and moving, they help prevent future injuries, especially in individuals prone to musculoskeletal problems.
7. Enhanced Athletic Performance
Athletes frequently rely on physiotherapy to enhance their performance and prevent injuries. Physiotherapists work with athletes to improve their flexibility, strength, and endurance while addressing imbalances or weaknesses that could lead to injury.
8. Improved Posture and Ergonomics
Many modern-day health problems stem from poor posture and ergonomics, particularly for individuals who spend long hours sitting at desks or using computers. Physiotherapy helps correct posture-related issues and educates patients on maintaining good ergonomic habits to avoid problems like neck strain, back pain, and repetitive strain injuries.
Types of Physiotherapy Treatments
Physiotherapy includes a variety of treatment methods, each tailored to the patient’s specific condition. Here are some common types of physiotherapy treatments:
1. Manual Therapy
Manual therapy involves hands-on techniques such as mobilization, manipulation, and soft tissue techniques to improve mobility, alleviate pain, and restore function.
2. Exercise Therapy
Exercise therapy is a core component of physiotherapy. It includes specific exercises that aim to restore strength, flexibility, balance, and coordination. These exercises are often part of rehabilitation programs for patients recovering from injuries or surgeries.
3. Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy uses electrical energy to stimulate nerves and muscles to reduce pain, improve circulation, and promote healing. Common electrotherapy modalities include Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS), ultrasound therapy, and laser therapy.
4. Heat and Cold Therapy
Physiotherapists use heat therapy to relax muscles and improve circulation, and cold therapy to reduce inflammation and numb pain. These techniques are often used in conjunction with other treatments to enhance recovery.
5. Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy, or aquatic therapy, involves exercising in water. The buoyancy of water helps reduce the load on joints, making it an ideal treatment for patients with arthritis or those recovering from joint surgery.
6. Vestibular Rehabilitation
For patients with balance issues or dizziness caused by vestibular disorders, vestibular rehabilitation exercises are designed to improve stability and reduce symptoms.
Common Conditions Treated by Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is used to treat a wide range of conditions, including:
1. Musculoskeletal Issues
Conditions like back pain, neck pain, sprains, strains, arthritis, and sports injuries are commonly treated with physiotherapy. Treatment helps relieve pain, improve mobility, and prevent recurrence.
2. Neurological Disorders
Neurological conditions such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and spinal cord injuries can result in impaired movement and function. Physiotherapy helps improve motor control, coordination, and balance in patients with these conditions.
3. Cardiopulmonary Conditions
Patients with heart and lung conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and post-heart attack recovery, benefit from physiotherapy through exercises that improve lung capacity, endurance, and cardiovascular health.
4. Orthopedic Conditions
Orthopedic conditions such as fractures, post-joint replacement recovery, ligament repairs, and rotator cuff injuries often require extensive physiotherapy to restore function and strength.
5. Geriatric Issues
As people age, they may experience problems with mobility, balance, and strength. Physiotherapy helps older adults maintain their independence and manage age-related issues such as osteoporosis and joint stiffness.
6. Pediatric Physiotherapy
Children with developmental delays, cerebral palsy, or muscular dystrophy can benefit from physiotherapy to improve their movement, strength, and coordination. Pediatric physiotherapists create age-appropriate treatment plans to address the unique needs of children.

Conclusion
Physiotherapy is a versatile and essential healthcare service that helps individuals recover from injury, manage chronic conditions, and improve their overall physical function. By addressing the root causes of pain and mobility issues, physiotherapy provides long-term solutions that enhance quality of life.
Whether you’re an athlete seeking to improve performance, a post-surgery patient looking to regain mobility, or someone managing a chronic illness, physiotherapy offers a tailored approach to health and wellness. Its benefits are wide-reaching, making it a key component of modern healthcare.
FAQs
Q1. What conditions can physiotherapy treat?
A. Physiotherapy can treat a wide range of conditions, including musculoskeletal problems like back pain, sports injuries, and arthritis, as well as neurological, cardiopulmonary, and orthopedic issues.
Q2. Is physiotherapy painful?
A.Physiotherapy treatments are generally not painful, although some techniques may cause mild discomfort, especially when working on stiff or injured areas. Physiotherapists work with patients to ensure their comfort and adapt treatments as needed.
Q3. How long does it take to see results from physiotherapy?
The duration of physiotherapy varies depending on the condition being treated. Some patients may notice improvements within a few sessions, while others may require several weeks or months of therapy.
Q4. Do I need a referral to see a physiotherapist?
A.In many countries, you can see a physiotherapist without a referral. However, some insurance plans may require a referral from a doctor for coverage.
Q5. How often should I go to physiotherapy?
The frequency of physiotherapy sessions depends on your condition and the treatment plan recommended by your physiotherapist. It may range from once a week to multiple times a week, depending on your needs.
Q6. Can physiotherapy help prevent injuries?
Yes, physiotherapy is highly effective in preventing injuries by improving strength, flexibility, and posture. Physiotherapists can provide personalized exercises and advice on injury prevention techniques.
Q7. Is physiotherapy suitable for children?
A.Yes, pediatric physiotherapy is designed specifically for children with developmental delays, injuries, or congenital conditions. Physiotherapists use age-appropriate treatments to help children improve their movement and strength.
Q8. What should I wear to physiotherapy sessions?
It’s best to wear loose, comfortable clothing that allows for easy movement. You may also need to bring any relevant medical records or imaging studies to your first appointment.